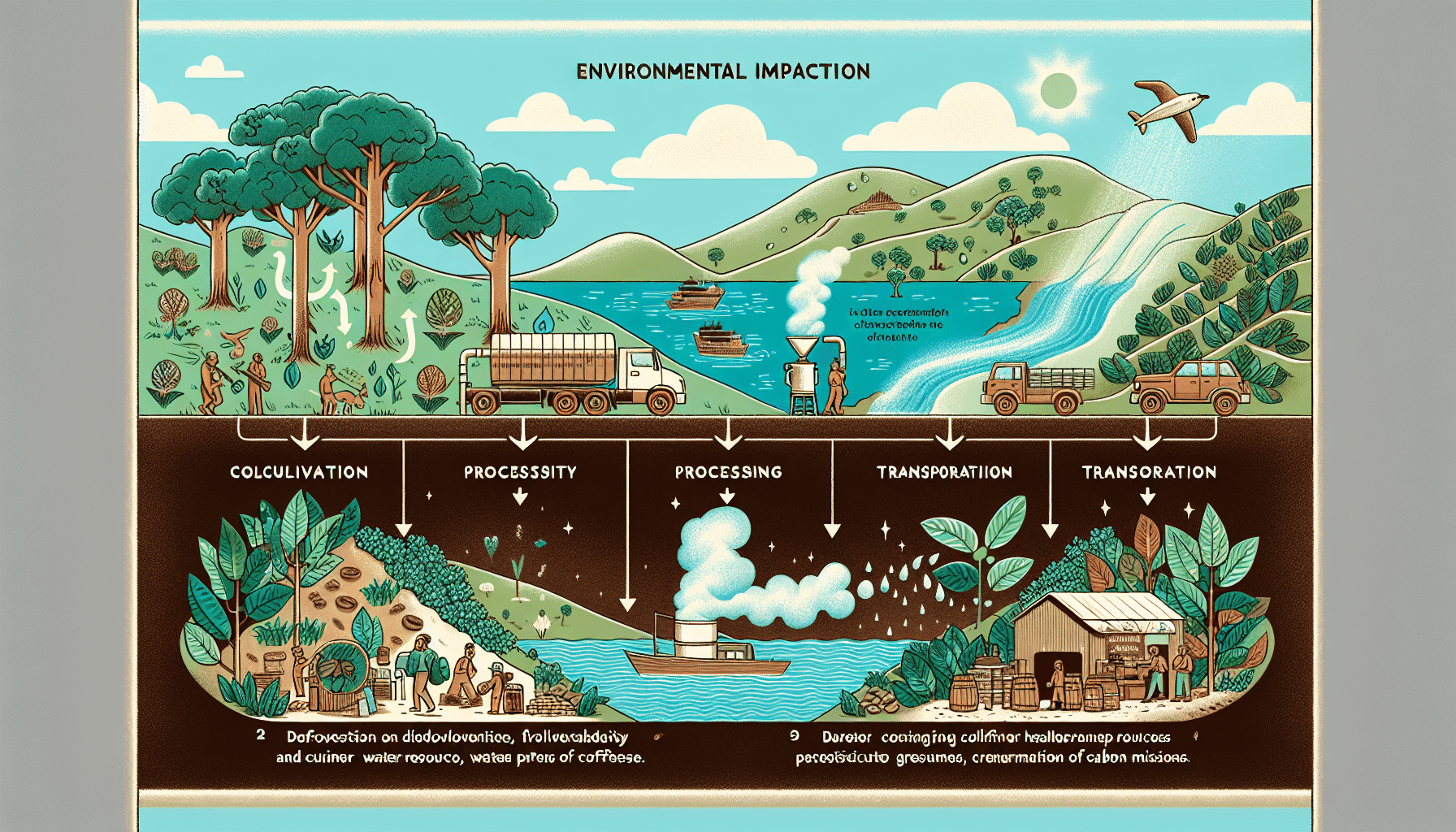
Coffee production may be a beloved industry, but it is not without its environmental consequences. In our comprehensive analysis, we delve into the intricate web of factors that contribute to the environmental impacts of coffee production. From deforestation and habitat destruction to water pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, the coffee industry has a significant footprint on our planet. By shedding light on these issues, we hope to inspire a discussion on sustainable practices and encourage consumers, producers, and policymakers to take action.

Deforestation
Coffee is one of the most popular beverages in the world, and its production has far-reaching consequences for the environment. One of the major environmental impacts of coffee production is deforestation. In order to make way for coffee plantations, vast areas of land are cleared of trees and other vegetation. This clearing of land not only disrupts natural ecosystems but also contributes to the loss of biodiversity.
Clearing of land for coffee plantations
To meet the increasing demand for coffee, large-scale deforestation takes place in coffee-growing regions around the world. Forests are cut down and cleared to make space for coffee farms. This results in the destruction of habitats for numerous plant and animal species, leading to the loss of biodiversity. The loss of forests also has a negative impact on carbon sequestration, as trees play a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Loss of biodiversity
Deforestation for coffee plantations leads to a significant loss of biodiversity. As forests are replaced by monoculture coffee farms, the diverse range of species that once called these forests home are displaced or lost entirely. This loss of biodiversity has a cascading effect on the entire ecosystem, as each species plays a unique and important role in maintaining ecological balance. Moreover, the destruction of habitats can lead to the endangerment or extinction of certain species, which further disrupts the delicate web of life.
Increased carbon emissions
The clearing of land for coffee plantations not only causes the loss of trees but also releases a substantial amount of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. When trees are cut down or burned, the carbon stored in their wood is released into the air as CO2. This contributes to the greenhouse effect and exacerbates climate change. With coffee production expanding worldwide, the cumulative impact of deforestation for coffee farming on carbon emissions is a serious concern.
Water Pollution
Coffee production also has significant impacts on water resources, leading to water pollution and degradation. The various activities associated with coffee farming, processing, and waste management contribute to the contamination of water sources.
Chemical runoff from coffee farms
Many coffee farms use chemical fertilizers, herbicides, and pesticides to maximize yields and protect crops from pests and diseases. However, these chemicals can seep into the soil and eventually find their way into nearby water bodies, such as rivers and streams. The runoff from coffee farms can contain high concentrations of harmful chemicals, which pollute the water and pose a risk to aquatic ecosystems.
Contamination of water sources
The pollution of water sources due to coffee production can have severe consequences for both human and aquatic life. The presence of chemicals in water bodies can harm fish, amphibians, and other aquatic organisms, disrupting ecosystems and reducing biodiversity. Moreover, contaminated water sources can affect human populations that rely on these water bodies for drinking, bathing, and irrigation. Exposure to pollutants in the water can lead to various health problems, both acute and chronic.
Impact on aquatic ecosystems
Water pollution from coffee production can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems. Chemicals that enter water bodies can accumulate in the sediments and persist for a long time, posing a threat to aquatic organisms. The presence of these pollutants can disrupt the natural balance of ecosystems, causing harm to fish, amphibians, and invertebrates. In turn, this can have cascading effects on higher trophic levels, impacting the overall health and functioning of aquatic ecosystems.
Soil Degradation
Coffee farming practices can also lead to soil degradation, compromising its fertility and productivity. The intensive cultivation of coffee and certain agricultural practices contribute to erosion, sedimentation, and the loss of valuable nutrients in the soil.
Loss of soil fertility
Coffee plants require specific soil conditions to thrive and produce high-quality beans. However, continuous cultivation and improper land management practices can deplete the soil of nutrients essential for plant growth. Without proper replenishment of these nutrients, the soil becomes less fertile over time, impacting the health and productivity of coffee plants. This loss of soil fertility not only affects coffee production but also increases the reliance on synthetic fertilizers, exacerbating environmental issues.
Erosion and sedimentation
Coffee farming often involves clearing large areas of land, leaving the soil exposed to erosion by wind and water. The removal of vegetation cover, such as trees and shrubs, reduces the natural protection against soil erosion. Consequently, rainwater washes away the topsoil, carrying sedimentation into nearby water bodies and affecting their quality. Erosion and sedimentation not only degrade the soil but also harm aquatic ecosystems, contributing to water pollution and habitat destruction.
Decreased agricultural productivity
Soil degradation resulting from coffee production practices has long-term consequences for agricultural productivity. As the soil loses its fertility and becomes more compacted, the ability of coffee plants to access nutrients and water is compromised. This leads to reduced yields and requires farmers to employ additional measures, such as increased fertilizer use, to sustain productivity. The decreased agricultural productivity also threatens food security in coffee-growing regions, as the focus on coffee production often comes at the expense of cultivating other crops.
Pesticide Use
The use of pesticides in coffee farming presents significant environmental concerns. While pesticides aim to control pests, diseases, and weeds, they can have harmful effects on human health, wildlife, and the environment as a whole.
Harmful effects on human health
Pesticides used in coffee farming can pose serious risks to human health. Workers who handle these chemicals are directly exposed to their toxic effects. Prolonged and continuous exposure to pesticides can lead to various health issues, including respiratory problems, skin irritations, and even more severe conditions such as cancer. Additionally, pesticide residues may persist on coffee beans, potentially exposing consumers to these harmful substances.
Toxicity to wildlife
The use of pesticides in coffee farms can have adverse effects on wildlife. Birds, insects, and mammals may come into contact with these chemicals through direct exposure or through contaminated food and water sources. Pesticides can interfere with reproductive systems, disrupt natural behavior patterns, and even lead to population declines in sensitive species. The loss of biodiversity caused by pesticide use can further disrupt ecosystems and negatively impact the natural balance of coffee-growing regions.
Residual pesticide presence in coffee beans
Pesticide residues can be present in coffee beans even after they have been harvested and processed. This residual presence raises concerns over potential health risks for consumers. The accumulation of pesticide residues in the human body has been linked to various health problems, including developmental issues, hormonal imbalances, and adverse effects on the nervous and immune systems. Minimizing pesticide use and implementing sustainable farming practices are crucial for reducing the presence of residues in coffee beans and safeguarding consumer health.

Energy Consumption
Coffee production involves various energy-intensive processes, from the processing and packaging of coffee to its transportation and distribution. The high energy consumption associated with coffee production contributes to carbon emissions and environmental degradation.
Processing and packaging of coffee
The processing of coffee beans involves several energy-intensive steps, such as roasting, grinding, and packaging. The machinery and equipment used in these processes consume significant amounts of energy, often derived from non-renewable sources. Additionally, the packaging materials, including bags, capsules, and single-use containers, contribute to the overall energy footprint of coffee production. Reducing energy consumption in these stages and adopting more sustainable packaging alternatives can help mitigate the environmental impacts.
Transportation and logistics
Coffee is a globally traded commodity, and its transportation from coffee farms to consumer markets involves long distances and multiple modes of transportation. The transportation of green coffee beans, roasted coffee, and packaged products requires significant amounts of energy. This energy consumption contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. By optimizing transportation routes, improving efficiency, and utilizing more sustainable transportation options, the environmental impact of coffee transportation can be reduced.
Carbon footprint of coffee production
The energy consumption and associated carbon emissions throughout the coffee production chain contribute to the carbon footprint of coffee. From the cultivation of coffee plants to the final consumption of brewed coffee, each stage involves the release of greenhouse gases. The carbon footprint of coffee production varies depending on factors such as farming practices, processing methods, and transportation distances. Adopting sustainable practices, investing in renewable energy sources, and promoting carbon offset initiatives can help reduce the carbon footprint of coffee production.
Waste Generation
Coffee production generates a significant amount of waste, ranging from byproducts of processing to packaging materials. The management of coffee waste presents numerous challenges and contributes to environmental pollution.
Coffee cherry pulp and husk waste
During the processing of coffee beans, the outer layers of the fruit, such as the pulp and husk, are removed and often discarded as waste. This organic waste is highly abundant and can pose environmental challenges if not properly managed. The decomposition of coffee waste can release methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. By implementing sustainable waste management practices, such as composting and utilizing waste as a source of renewable energy, the environmental impact of coffee waste can be minimized.
Packaging waste
The packaging materials used in the coffee industry, such as plastic bags, capsules, and disposable cups, contribute to the generation of waste. These materials often end up in landfills or litter the environment, contributing to pollution and taking a significant amount of time to decompose. Adopting eco-friendly packaging alternatives, encouraging recycling initiatives, and promoting reusability can help reduce the amount of packaging waste generated by the coffee industry.
Disposal challenges
The disposal of coffee waste, particularly organic waste from processing and brewing, presents challenges due to its volume and potential environmental impact. If not managed properly, coffee waste can contaminate soil and water sources, contributing to pollution and ecosystem disruption. To address these challenges, coffee producers and consumers should prioritize waste reduction, employ sustainable disposal methods such as composting, and support initiatives that promote circular economy models in the coffee industry.

Climate Change
Coffee production is highly vulnerable to climate change, and the effects of a changing climate pose significant challenges for coffee-growing regions worldwide. Rising temperatures, altered rainfall patterns, and extreme weather events can have detrimental impacts on coffee crops.
Vulnerability of coffee crops to temperature changes
Coffee plants have very specific temperature requirements for optimal growth and bean development. Higher temperatures due to climate change can disrupt these requirements, potentially leading to reduced yields and lower-quality beans. Additionally, warmer temperatures can favor the spread of pests and diseases, posing further threats to coffee crops. The vulnerability of coffee crops to temperature changes highlights the need for adaptation strategies and sustainable farming practices to mitigate the negative impacts of climate change.
Altered rainfall patterns
Changes in rainfall patterns, both in terms of timing and quantity, can significantly affect coffee production. Coffee plants require well-distributed rainfall throughout the growing season for proper growth and fruit development. Climate change can lead to shifts in rainfall patterns, including more frequent droughts or intense rainfall events. These changes can have negative consequences for coffee farmers, as droughts can lead to water scarcity, while heavy rainfall can cause soil erosion and increase the risk of diseases. Adapting irrigation practices, water conservation measures, and improving soil management can help coffee farmers cope with altered rainfall patterns.
Impact on coffee-growing regions
Climate change poses a significant threat to coffee-growing regions around the world. Many of these regions are already located in areas with fragile ecosystems and limited resources. The changing climate can further exacerbate the environmental challenges faced by these regions, leading to decreased productivity, economic instability, and social disruption. It is crucial for the coffee industry to invest in climate adaptation strategies, promote sustainable land management practices, and support farmers in vulnerable regions to ensure the long-term sustainability of coffee production.
Water Scarcity
Coffee production requires substantial amounts of water, and its cultivation can contribute to water scarcity, particularly in arid regions. The high water demand of coffee farming, coupled with competition for water resources, presents significant challenges in terms of sustainability.
High water demand for irrigation
Coffee plants require adequate water for optimal growth and bean development. In many coffee-producing regions, irrigation is necessary to meet this demand, particularly during dry periods or in arid environments. The extensive irrigation required for coffee farming can put significant pressure on water resources, depleting local water supplies and contributing to water scarcity. Implementing water-efficient irrigation systems, promoting water conservation practices, and exploring alternatives to water-intensive coffee production can help mitigate the impacts of water scarcity.
Competition for water resources
Water scarcity in coffee-growing regions can lead to increased competition for limited water resources. Local communities, agriculture, and other industries often depend on the same water sources as coffee farms, creating conflicts over water allocation. This competition for water can have social and economic implications, as well as environmental consequences. Balancing the water needs of different stakeholders, implementing integrated water management practices, and involving local communities in decision-making processes are vital for ensuring the sustainability of coffee production amidst water scarcity.
Sustainability of coffee production in arid regions
Coffee cultivation in arid regions faces unique challenges due to limited water availability. The sustainability of coffee production in these regions requires careful consideration of water resources and efficient water management practices. Diversifying crops, introducing agroforestry techniques, and implementing innovative irrigation methods, such as drip irrigation or rainwater harvesting, can help reduce water demand and improve water use efficiency. Working in collaboration with local communities, governments, and international organizations is crucial for ensuring the long-term viability of coffee production in arid regions while addressing water scarcity concerns.
Loss of Habitat
The expansion of coffee production often involves the conversion of natural habitats into coffee farms, leading to the loss of valuable ecosystems. The destruction of habitats not only displaces wildlife but also poses a threat to endangered species.
Conversion of natural habitats to coffee farms
As the demand for coffee grows, natural habitats in coffee-growing regions are being cleared and converted into coffee plantations. This conversion often involves the removal of native vegetation, including forests and other natural ecosystems, to make way for coffee farms. The loss of natural habitats disrupts the intricate web of life, displacing numerous plant and animal species and fragmenting ecosystems. This habitat loss has far-reaching consequences for biodiversity, as many species depend on intact habitats for their survival.
Displacement of wildlife
The conversion of natural habitats to coffee farms displaces wildlife, forcing animals to either adapt to their new surroundings or seek new habitats. This displacement disrupts migration patterns, alters animal behavior, and increases competition for resources in the remaining fragments of natural habitat. As coffee production expands, the displacement of wildlife can lead to population declines, fragmentation, and even local extinctions. It is crucial to consider the conservation of natural habitats and the protection of wildlife when expanding coffee production.
Threat to endangered species
The loss of natural habitats due to coffee farming poses a significant threat to endangered species. Many coffee-growing regions are home to unique and vulnerable plant and animal species, some of which are already critically endangered. The destruction of habitats and the resulting habitat fragmentation further jeopardize the survival of these species. Protecting and restoring natural habitats, implementing sustainable land use practices, and promoting biodiversity conservation in coffee-growing regions are essential for mitigating the threat to endangered species and maintaining ecosystem health.
Social Impacts
The environmental impacts of coffee production are closely intertwined with social issues, particularly in coffee-producing communities. Exploitation of coffee laborers, social inequality, and human rights issues are among the social challenges faced by the coffee industry.
Exploitation of coffee laborers
In many coffee-producing regions, labor conditions and worker rights are pressing concerns. Coffee laborers often face low wages, long and exhausting working hours, inadequate safety measures, and limited access to essential services and social protections. The exploitation of coffee laborers not only undermines social justice but also perpetuates cycles of poverty and inequality. Ensuring fair and ethical labor practices, improving working conditions, and promoting social responsibility within the coffee industry are necessary steps to address these social issues.
Social inequality in coffee-producing communities
The benefits and profits from coffee production are often concentrated in the hands of a few, exacerbating social and economic inequalities within coffee-producing communities. Smallholder farmers, who make up a significant portion of the coffee industry, face numerous challenges such as limited access to resources, market volatility, and inadequate infrastructure. The prevalence of social inequality hampers the well-being and development of these communities. Building inclusive and sustainable value chains, supporting small-scale farmers, and fostering partnerships that prioritize fair trade and economic empowerment are crucial for tackling social inequality in the coffee industry.
Human rights issues in the coffee industry
Human rights abuses, such as child labor, forced labor, and unsafe working conditions, persist in some coffee-producing regions. The prevalence of these issues reflects systemic problems within the coffee industry, including insufficient regulation, lack of transparency, and limited accountability. Combatting human rights issues requires a multi-stakeholder approach that involves governments, industry players, and civil society organizations. Implementing and enforcing robust social standards and certification schemes, empowering local communities, and promoting transparency and traceability throughout the coffee supply chain are essential for eradicating human rights abuses in the coffee industry.
In conclusion, the production of coffee has significant environmental impacts, ranging from deforestation and loss of biodiversity to water pollution, soil degradation, and climate change. The use of pesticides, high energy consumption, waste generation, water scarcity, loss of habitat, and social issues further magnify the environmental footprint of coffee production. Addressing these impacts requires a holistic approach that embraces sustainable and responsible practices throughout the entire coffee supply chain, from farm to cup. By promoting sustainable farming methods, protecting natural habitats, managing water resources responsibly, and prioritizing social welfare, the coffee industry can minimize its environmental footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future.